Bromocriptine Information
Click here to view all Bromocriptine productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
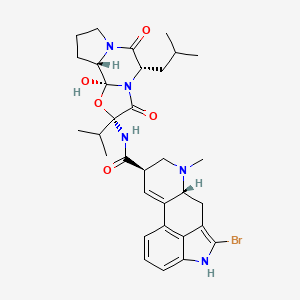
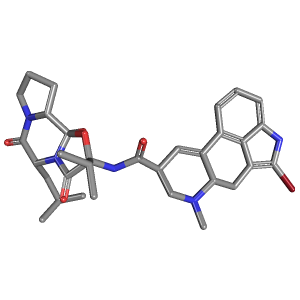
Bromocriptine is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called dopamine agonists. It is primarily used to treat conditions caused by an excess of the hormone prolactin in the body, such as hyperprolactinemia, prolactin-secreting tumors (prolactinomas), and certain menstrual problems.
Bromocriptine works by binding to dopamine receptors in the brain, specifically the D2 receptor subtype. By stimulating these receptors, it mimics the action of dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in various functions including regulating the release of prolactin. By increasing dopamine activity, bromocriptine suppresses the production and release of prolactin from the pituitary gland, thereby reducing prolactin levels in the body.
Additionally, bromocriptine has been used off-label for other conditions such as Parkinson's disease, acromegaly (excess growth hormone), and type 2 diabetes. In these cases, its mechanism of action involves stimulating dopamine receptors in different regions of the brain to help regulate motor control and improve insulin sensitivity.
Synonyms of Bromocriptine
- bromocriptine
- 25614-03-3
- Bromocryptine
- Bromocriptin
- Bromoergocryptine
- Bromergocryptine
- Bromoergocriptine
- 2-Bromo-alpha-ergocryptine
- Parlodel
- 2-Bromo-alpha-ergokryptine
- Bromocriptina
- Bromocriptinum
- Ergoset
- 2-Bromo-alpha-ergokryptin
- Bromocriptinum [INN-Latin]
- Bromocriptina [INN-Spanish]
- Ergocryptine, 2-bromo-
- Bromocryptin
- CB-154
- 2-Bromoergocryptine
- 2-Bromoergokryptine
- Bagren
- Bromocriptine methanesulfonate
- C32H40BrN5O5
- CCRIS 3244
- Bromocriptine [BAN]
- Bromocriptine [USAN:BAN:INN]
- 2-Bromoergocryptine Methanesulfonate
- EINECS 247-128-5
- Bromocriptine (USAN/INN)
- ergolactin
- UNII-3A64E3G5ZO
- 3A64E3G5ZO
- Bromocriptine (mesylate)
- CHEBI:3181
- Ergotaman-3',6',18-trione, 2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-, (5'alpha)-
- Bromocriptine [USAN:INN:BAN]
- DTXSID1022687
- SANDOZ 15-754
- 2-bromoergocriptine
- 2-Bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'-alpha-(2-methylpropyl)ergotamin-3',6',18-trione
- Parlodel (TN)
- (+)-Bromocriptine
- (5'alpha)-2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-3',6',18-trioxoergotaman
- (5'alpha)-2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'-(2-methylpropyl)ergotaman-3',6',18-trione
- Ergotaman-3',6',18-trione, 2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-, (5'.alpha.)-
- 2-Bromo-.alpha.-ergocryptine
- Apo-Bromocriptine
- Parlodel Snaptabs
- Alti-Bromocriptine
- (5'alpha)-2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-5'-isobutyl-2'-isopropyl-3',6',18-trioxoergotaman
- (5'alpha)-2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-2'-(propan-2-yl)-3',6',18-trioxoergotaman
- (6aR,9R)-5-Bromo-N-((2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-10b-hydroxy-5-isobutyl-2-isopropyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-2H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl)-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide
- (6aR,9R)-5-bromo-N-[(1S,2S,4R,7S)-2-hydroxy-7-(2-methylpropyl)-5,8-dioxo-4-propan-2-yl-3-oxa-6,9-diazatricyclo[7.3.0.02,6]dodecan-4-yl]-7-methyl-6,6a,8,9-tetrahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide
- NSC169774
- Bromokryptine
- SR-01000075356
- NCGC00024584-03
- 08Y
- Bromocriptine+ (GTP-)
- Prestwick0_000121
- Prestwick1_000121
- Prestwick2_000121
- Carboprost Methylate,(S)
- BROMOCRIPTINE [MI]
- Biomol-NT_000005
- CHEMBL493
- D06YFA
- GTPL35
- BROMOCRIPTINE [INN]
- BROMOCRIPTINE [USAN]
- Lopac0_000171
- SCHEMBL25297
- BROMOCRIPTINE [VANDF]
- BIDD:GT0464
- SPBio_002101
- BROMOCRIPTINE [WHO-DD]
- BPBio1_001131
- DTXCID602687
- Ergocryptine, 2-bromo-(8CI)
- BDBM81993
- C32-H40-Br-N5-O5
- Tox21_110907
- PDSP2_001500
- AKOS015961273
- CCG-204266
- DB01200
- SDCCGSBI-0050159.P003
- dioxooctahydro-2H-oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo
- NCGC00024584-04
- NCGC00024584-05
- NCGC00024584-07
- NCGC00024584-09
- AC-13601
- Ergotaman-3',6',18-trione, 2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'alpha-(2-methylpropyl)-
- LS-64540
- NCI60_001365
- 10b-hydroxy-5-isobutyl-2-isopropyl-3,6-
- CAS-25614-03-3
- C06856
- D03165
- hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide
- EN300-19768234
- Q413581
- J-016067
- SR-01000075356-5
- (6aR,9R)-5-bromo-N-((2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-
- [2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl)-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-
- BRD-K14496212-001-01-1
- BRD-K14496212-066-04-8
- SAN 15-754; Sandoz 15-754; -Bromocryptine; -Bromoergocryptine; -Ergolactin
- (4R,7R)-10-bromo-N-[(1S,2S,4R,7S)-2-hydroxy-7-(2-methylpropyl)-5,8-dioxo-4-(propan-2-yl)-3-oxa-6,9-diazatricyclo[7.3.0.0^{2,6}]dodecan-4-yl]-6-methyl-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0^{2,7}.0^{12,16}]hexadeca-1(15),2,9,12(16),13-pentaene-4-carboxamide
- (4R,7R)-10-bromo-N-[(1S,2S,4R,7S)-2-hydroxy-7-(2-methylpropyl)-5,8-dioxo-4-(propan-2-yl)-3-oxa-6,9-diazatricyclo[7.3.0.0^{2,6}]dodecan-4-yl]-6-methyl-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0^{2,7}.0^{12,16}]hexadeca-1(16),2,9,12,14-pentaene-4-carboxamide
- (5'-alpha)-2-Bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'-(2-methylpropyl)ergotaman-3',6',18-trione
- Ergotaman-3',6',18-trione, 2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1- methylethyl)-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-, (5'?)-
- Ergotaman-3',6',18-trione, 2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-2'-(1-methylethyl)-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-,(5'-alpha)-
- N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-10b-hydroxy-5-isobutyl-2-isopropyl-3,6-dioxo-8,9,10,10a-tetrahydro-5H-oxazolo[[?]]pyrrolo[[?]]pyrazin-2-yl]-bromo-methyl-[?]carboxamide

