Clenbuterol HCL Information
Click here to view all Clenbuterol HCL productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
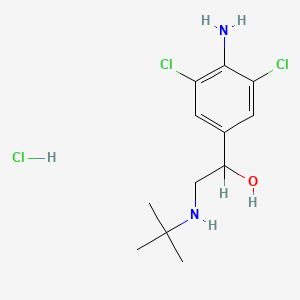
Clenbuterol Hydrochloride (HCL), commonly known as Clenbuterol, is a sympathomimetic amine and bronchodilator that is often used for its thermogenic and performance-enhancing properties. Here are some details about Clenbuterol HCL:
- Medical Use: Clenbuterol was initially developed as a medication for the treatment of respiratory conditions, such as asthma. It acts as a bronchodilator, which means it relaxes and widens the airways in the lungs, making it easier to breathe. However, its medical use in humans is limited and varies by country.
- Thermogenic Effects: Clenbuterol is commonly used off-label as a weight loss and bodybuilding aid due to its thermogenic properties. It stimulates beta-2 adrenergic receptors, leading to an increase in body temperature and metabolic rate. This can result in enhanced calorie burning, fat loss, and potentially improved athletic performance.
- Performance Enhancement: Athletes and bodybuilders may use Clenbuterol to promote lean muscle retention and improve physical performance. It is believed to enhance oxygen transportation, increase aerobic capacity, and help preserve muscle mass during periods of calorie restriction or intense training.
- Dosage and Administration: Clenbuterol is typically taken orally in tablet or liquid form. The dosage and cycle duration can vary depending on individual needs, goals, and tolerance. However, it's important to note that Clenbuterol is not approved for human use in many countries, including the United States, and its non-medical use is considered illegal.
- Side Effects: Clenbuterol can have various side effects, which may include increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, nervousness, tremors, sweating, insomnia, headaches, muscle cramps, and nausea. These effects are typically dose-dependent and can vary among individuals. Long-term or excessive use of Clenbuterol may lead to more serious cardiovascular and systemic complications.
- Legal Status: Clenbuterol is classified as a controlled substance and is subject to legal restrictions in many countries. It is important to be aware of the legal status and regulations concerning the possession, sale, and use of Clenbuterol in your jurisdiction.
It's essential to emphasize that the use of Clenbuterol for non-medical purposes and without the supervision of a healthcare professional is considered unsafe and illegal. Misuse and abuse of Clenbuterol can lead to serious health risks and adverse effects.
Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional for accurate information and guidance regarding the appropriate and legal use of medications for your specific needs.
How Clenbuterol HCL works?
Clenbuterol Hydrochloride (HCL) works primarily through its interaction with beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the body. Here's how Clenbuterol HCL works:
- Activation of Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptors: Clenbuterol is a sympathomimetic amine, which means it mimics the effects of the sympathetic nervous system. It selectively binds to and activates beta-2 adrenergic receptors found in various tissues, including the bronchial smooth muscles, fat cells, and skeletal muscle.
- Bronchodilation: Clenbuterol's initial medical application was for the treatment of respiratory conditions like asthma. By binding to beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the bronchial smooth muscles, it causes relaxation and widening of the airways. This leads to bronchodilation, making breathing easier for individuals with respiratory disorders.
- Increased Metabolic Rate: Clenbuterol's activation of beta-2 adrenergic receptors in fat cells can stimulate lipolysis, which is the breakdown of stored triglycerides (fat) into free fatty acids. The liberated fatty acids can then be used as an energy source. This process increases the metabolic rate and promotes fat loss.
- Thermogenesis: Through its interaction with beta-2 adrenergic receptors, Clenbuterol stimulates the mitochondria in cells to produce more heat. This effect is known as thermogenesis and is associated with an increase in body temperature. Thermogenesis can enhance calorie expenditure and potentially contribute to weight loss.
- Anabolic Effects: Clenbuterol has been suggested to have anabolic properties, although the mechanisms are not fully understood. Some studies indicate that it may promote muscle protein synthesis and inhibit protein degradation, potentially leading to muscle preservation and growth. However, further research is needed to fully establish these effects in humans.
It's important to note that the use of Clenbuterol for non-medical purposes and without the supervision of a healthcare professional is considered unsafe and illegal in many countries. Clenbuterol can have significant side effects and health risks, particularly when used inappropriately or at high doses. It's crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for accurate information and guidance regarding the use of medications and substances for your specific needs.
Synonyms of Clenbuterol HCL
- Clenbuterol hydrochloride
- 21898-19-1
- Clenbuterol HCl
- Spiropent
- Ventipulmin
- Clenbuterol-D9 HCl
- Clenbuterol clorhidrato
- NAB-365Cl
- GOR5747GWU
- 1-(4-amino-3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2-(tert-butylamino)ethanol;hydrochloride
- NAB-365
- MLS000069838
- NAB 365 CL
- CHEBI:31410
- SMR000058854
- 21898-19-1 (HCl)
- 1-(4-amino-3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2-(tert-butylamino)ethanol hydrochloride
- Planipart hydrochloride
- 4-Amino-alpha-(tert-butylaminomethyl)-3,5-dichlorobenzyl Alcohol Hydrochloride
- 4-Amino-alpha-((tert-butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dichlorobenzyl alcohol hydrochloride
- Clenbuterol clorhidrato [Spanish]
- EINECS 244-643-7
- C12H18Cl2N2O.xClH
- SR-01000721909
- Contrasmina
- Clenasma
- Siropent
- C12-H18-Cl2-N2-O.x-Cl-H
- Spiropent (TN)
- Prestwick_761
- clenbuterolhydrochloride
- 4-AMINO-.ALPHA.-((TERT-BUTYLAMINO)METHYL)-3,5-DICHLOROBENZYL ALCOHOL
- 4-Amino-alpha-((tert-butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dichlorobenzyl alcoholmonohydrochloride
- 4-Amino-alpha-((tert-butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dichlorobenzylalkohol-hydrochlorid [German]
- Benzyl alcohol, 4-amino-alpha-((tert-butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dichloro-, monohydrochloride
- Opera_ID_146
- UNII-GOR5747GWU
- clenbuterol monohydrochloride
- MLS001148242
- MLS002222258
- Clenbuterol Hydrochloride,(S)
- SCHEMBL123545
- SPECTRUM1503917
- (+-)-clenbuterol hydrochloride
- CHEMBL1330729
- DTXSID60944496
- REGID_for_CID_5702273
- Clenbuterol hydrochloride, >=95%
- HMS1569E11
- Pharmakon1600-01503917
- (+-)-clenbuterol monohydrochloride
- BCP13609
- HY-B1614
- EINECS 274-226-5
- CCG-39893
- Clenbuterol hydrochloride (JAN/USP)
- Clenbuterol hydrochloride [USP:JAN]
- MFCD00083280
- NSC758633
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [MI]
- AKOS007930709
- AM84776
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [JAN]
- CS-6917
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [MART.]
- NCGC00095982-01
- AC-11159
- AS-12537
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [USP-RS]
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [WHO-DD]
- LS-30603
- C2691
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [GREEN BOOK]
- VU0244438-4
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [EP IMPURITY]
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [EP MONOGRAPH]
- D01360
- F17351
- CLENBUTEROL HYDROCHLORIDE [USP MONOGRAPH]
- Q-200872
- SR-01000721909-4
- SR-01000721909-5
- 1-(4-amino-3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2-(tert-butylamino)
- Q27114305
- Clenbuterol Hydrochloride 1.0 mg/ml in Dimethyl Sulfoxide (as free base)
- Clenbuterol hydrochloride, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- (1)-4-Amino-alpha-((tert-butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dichlorobenzyl alcohol monohydrochloride
- 4-amino-3,5-dichloro-alpha-(((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)methyl)benzenemethanol hydrochloride
- 4-amino-alpha-((tert-butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dichlorobenzyl alcohol monohydrochloride
- 4-Amino-alpha-((tert-butylamino)methyl)-3,5-dichlorobenzylalkohol-hydrochlorid
- Clenbuterol hydrochloride, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
- 4-amino-3,5-dichloro-alpha-(((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)methyl)benzenemethanol monohydrochloride

