Duloxetine Information
Click here to view all Duloxetine productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
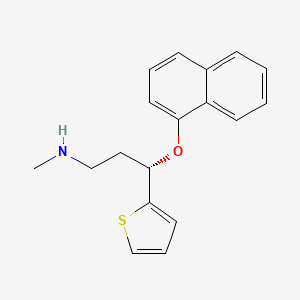
Duloxetine is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). It is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, fibromyalgia, and chronic musculoskeletal pain.
Duloxetine works by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. Serotonin and norepinephrine are neurotransmitters that play a role in regulating mood, emotions, and pain perception. By inhibiting their reuptake, duloxetine helps to maintain higher levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain, which can improve mood, reduce anxiety, and alleviate pain.
Additionally, duloxetine also has a weak effect on blocking the reuptake of dopamine, another neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation. This combined effect on serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine helps to restore the balance of these chemicals in the brain, leading to its therapeutic effects.
Synonyms of Duloxetine
- duloxetine
- 116539-59-4
- (S)-Duloxetine
- Cymbalta
- Yentreve
- (S)-N-Methyl-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)propan-1-amine
- Duloxetine [INN:BAN]
- LY 248686
- duloxetine, (+)-isomer
- HSDB 7368
- LY248686
- UNII-O5TNM5N07U
- O5TNM5N07U
- Duloxetine (INN)
- Yentreve (TN)
- CHEBI:36795
- methyl[(3S)-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)propyl]amine
- 2-Thiophenepropanamine, N-methyl-gamma-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, (gammaS)-
- (S)-N-Methyl-gamma-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-thiophenepropanamine
- (3S)-N-methyl-3-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-thiophen-2-ylpropan-1-amine
- LY-248686
- Duloxetine Boehringer Ingelheim
- DTXSID6048385
- (3S)-N-methyl-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propan-1-amine
- Cymbalta (TN)
- DULOXETINE [INN]
- 2-Thiophenepropanamine, N-methyl-gamma-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, (S)-
- (3S)-N-methyl-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propan-1-amine
- (3s)-N-Methyl-3-(Naphthalen-1-Yloxy)-3-(Thiophen-2-Yl)propan-1-Amine
- SMR000449282
- NCGC00164559-01
- duloxetinum
- Duloxetina
- 29E
- MFCD06801358
- CPD000449282
- 2-tiofenpropanamina, n-metil-?-(1-naftaleniloxi)-, clorhidrato (1:1), (?s)-
- DRIZALMA SPRINKLE
- DULOXETINE [MI]
- DULOXETINE [HSDB]
- DULOXETINE [VANDF]
- D01AXB
- SCHEMBL8291
- CHEMBL1175
- DULOXETINE [WHO-DD]
- GTPL202
- MLS000758267
- MLS001423946
- DULOXETINE [EMA EPAR]
- (S)-Duloxetine;LY248686
- DTXCID7028358
- N-Methyl-gama-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-thiophenepropanamine
- BDBM84745
- N06AX21
- (+)-(S)-N-Methyl-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propylamine monohydrochloride
- HMS2051I05
- HMS3886K11
- HY-B0161
- PDSP1_000969
- PDSP1_001385
- PDSP2_000953
- PDSP2_001369
- s5071
- AKOS015851058
- CCG-100763
- DB00476
- NC00013
- NCGC00164559-02
- NCGC00164559-04
- AC-15704
- AS-35259
- SBI-0206832.P001
- LS-172322
- CAS_136434-34-9
- D07880
- EN300-150640
- AB00639911-13
- AB00639911_15
- AB00639911_16
- Q411932
- J-003455
- J-523680
- (+)-(S)-N-Methyl-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propylamin
- (+)-(s)-n-methyl-gamma-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-thiophenepropylamine
- (+)-n-methyl-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propanamine
- (S)-(+)-N-methyl-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propylamine
- (S)-N-methyl-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-3-(2-thienyl) propanamine
- (+)-(S)-N-METHYL-gamma(1-NAPHTHYLOXY)-2-THIOPHENEPROPYLAMINE
- (3S)-N-methyl-3-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-thiophen-2-yl-propan-1 amine
- (3S)-N-methyl-3-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-thiophen-2-yl-propan-1-amine
- (3s)-n-methyl-3-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-thiophen-2-yl-propan-1amine
- (gamma-S)-N-Methyl-gamma-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-thiophenepropanamine
- (gammaS)-N-methyl-gamma-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-thiophenepropanamine
- (S)-(+)-N-methyl-3-(1-naphthaleneoxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propanamine
- (+)-(S)-N-METHYL-.GAMMA.(1-NAPHTHYLOXY)-2-THIOPHENEPROPYLAMINE
- 2-THIOPHENEPROPANAMINE, N-METHYL-.GAMMA.-(1-NAPHTHALENYLOXY)-, (S)-

