Epitalon Information
Click here to view all Epitalon productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
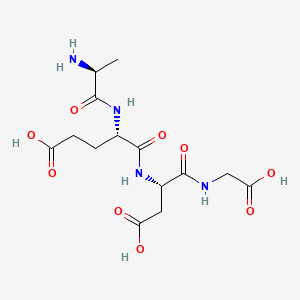
Epitalon, also known as epithalamin or epithalon, is a synthetic peptide made up of four amino acids: alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine. It was first isolated from the pineal gland of animals and later synthesized in a laboratory.
Epitalon is believed to have anti-aging properties and is often referred to as a "telomerase activator." Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten as cells divide and age. When telomeres become too short, cells can no longer divide, leading to cellular aging and eventual cell death. Telomerase is an enzyme that helps maintain the length of telomeres, and its activity declines with age.
Epitalon is thought to stimulate the production of telomerase, thereby potentially slowing down the aging process. By activating telomerase, it may help to lengthen telomeres and delay cellular aging. Additionally, Epitalon has been suggested to have other beneficial effects, such as improving sleep, regulating the endocrine system, and enhancing overall well-being.
However, it is important to note that the scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of Epitalon is limited and primarily based on animal studies and anecdotal reports. Further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and potential benefits in humans.
Synonyms of Epitalon
- Epitalon
- 307297-39-8
- Epithalon
- Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
- UNII-O65P17785G
- Glycine, L-alanyl-L-alpha-glutamyl-L-alpha-aspartyl-
- O65P17785G
- (4S)-4-[[(2S)-2-aminopropanoyl]amino]-5-[[(2S)-3-carboxy-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid
- 64082-79-7
- Epithalone
- Epithalamin
- Epithalamine
- C14H22N4O9
- C14-H22-N4-O9
- AE-0 peptide
- L-Alanyl-L-&Alpha
- L-Alanyl-L-glutamyl-L-aspartyl-glycine
- BDM-E
- D07JRL
- alanyl-glutamyl-aspartyl-glycine
- SCHEMBL5685928
- DTXSID80952957
- GLXC-25920
- BCP13981
- HY-P1149
- Retinal disease therapeutic, Biodiem
- AC-33517
- LS-72251
- CS-0028299
- Glycine, L-alanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-aspartyl-
- A14399
- Epitalon (Russian Academy of Medical Sciences)
- A876104
- Glycine, L-alanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-aspartyl- Acetate
- Q27285389
- GLYCINE, L-ALANYL-L-.ALPHA.-GLUTAMYL-L-.ALPHA.-ASPARTYL-

