Fluoxymesterone (Halotestin) Information
Click here to view all Fluoxymesterone (Halotestin) productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
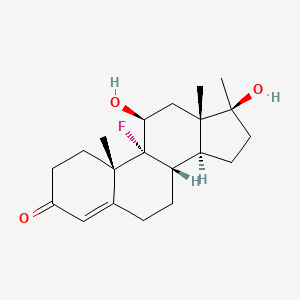
Fluoxymesterone, commonly known by its brand name Halotestin, is a synthetic androgenic-anabolic steroid. It is derived from testosterone and is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance due to its potential for abuse and misuse.
Fluoxymesterone is primarily used in the medical field to treat conditions such as delayed puberty in males and certain types of breast cancer in women. However, it is more commonly known for its use in the bodybuilding and athletic communities to enhance performance and increase muscle mass.
As an androgenic-anabolic steroid, Fluoxymesterone works by binding to androgen receptors in various tissues, including muscle cells. This binding activates the androgen receptors, leading to an increase in protein synthesis and nitrogen retention, which promotes muscle growth and strength. It also has a high affinity for the androgen receptors in the central nervous system, which can contribute to its effects on aggression and mood.
Additionally, Fluoxymesterone has a unique characteristic of being resistant to metabolism by the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen. This means that it does not convert to estrogen in the body, resulting in a reduced risk of estrogen-related side effects such as water retention and gynecomastia.
However, it is important to note that Fluoxymesterone carries several potential side effects, including liver toxicity, cardiovascular risks, suppression of natural testosterone production, and psychological effects such as aggression and mood swings. It should only be used under medical supervision and with a proper understanding of the potential risks involved.
Synonyms of Fluoxymesterone (Halotestin)
- fluoxymesterone
- 76-43-7
- Halotestin
- Fluoximesterone
- Fluoxymestrone
- Androfluorene
- Androfluorone
- Fluotestin
- Android-f
- Ora-Testryl
- Androsterolo
- Fluosterone
- Flusteron
- Flutestos
- Oralsterone
- Oratestin
- Testoral
- Ultandren
- Ultandrene
- Fluoximesteronum
- Neo-Ormonal
- Ora Testryl
- Fluoximesterona
- Fluossimesterone [DCIT]
- Fluoxymesteronum
- Anadroid-F
- Fluoxymesteronum [INN-Latin]
- Fluoximesterona [INN-Spanish]
- Fluoximesteron
- Fluossimesterone
- NSC-12165
- Fluoxymesteron
- Androxy
- (8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,17S)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-10,13,17-trimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta-hydroxy-17-methyltestosterone
- 9-Fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
- Halotestin (TN)
- Fluoxymesterone ciii
- U 6040
- CCRIS 9036
- component of Halodrin
- Fluoxymesterone [INN:BAN:JAN]
- HSDB 3333
- EINECS 200-961-8
- NSC 10704
- NSC-10704
- UNII-9JU12S4YFY
- Testosterone, 9-fluoro-11beta-hydroxy-17-methyl-
- BRN 2008796
- 9JU12S4YFY
- 9-alpha-Fluoro-11-beta-hydroxy-17-methyltestosterone
- 17-alpha-Methyl-9-alpha-fluoro-11-beta-hydroxytesterone
- AI3-52940
- CHEBI:5120
- FXM
- DTXSID8033512
- C20H29FO3
- 9-Fluoro-11-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
- 9alpha-Fluoro-17alpha-methyl-11beta,17-dihydroxy-4-androsten-3-one
- 11beta,17beta-Dihydroxy-9alpha-fluoro-17alpha-methyl-4-androsten-3-one
- 9-alpha-Fluoro-17-alpha-methyl-11-beta,17-dihydroxy-4-androsten-3-one
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17alpha-methyl-4-androstene-3-one
- 11-beta,17-beta-Dihydroxy-9-alpha-fluoro-17-alpha-methyl-4-androster-3-one
- 9-alpha-Fluoro-11-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-17-alpha-methyl-4-androstene-3-one
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-methyl-, (11beta,17beta)-
- 17alpha-Methyl-9alpha-fluoro-11beta-hydroxytesterone
- Fluoxymesterone [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]
- Fluoro-9-alpha dihydroxy-11-beta,17-beta methyl-17-alpha androstene-4 one-3 [French]
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methyl-
- (11beta,17beta)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
- 11beta,17beta-Dihydroxy-9alpha-fluoro-17alpha-methyl-4-androster-3-one
- Fluoro-9-alpha dihydroxy-11-beta,17-beta methyl-17-alpha androstene-4 one-3
- 4-08-00-02057 (Beilstein Handbook Reference)
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.-hydroxy-17-methyltestosterone
- DTXCID6013512
- 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17alpha-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methyl- (VAN)
- 9.alpha.-Fluoro-11.beta.,17.beta.-dihydroxy-17.alpha.-methyl-4-androstene-3-one
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-methyl-, (11.beta.,17.beta.)-
- CAS-76-43-7
- (8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,17S)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-10,13,17-trimethyl-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3(2H)-one
- Testosterone, 9-fluoro-11.beta.-hydroxy-17-methyl-
- fluoxymesteron-
- NCGC00182970-01
- Androxy (TN)
- D0L2LS
- SCHEMBL5096
- CHEMBL1445
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [MI]
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [INN]
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [JAN]
- MLS001055414
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [HSDB]
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [VANDF]
- GTPL2861
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [MART.]
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [WHO-DD]
- BDBM18189
- Fluoxymesterone (JAN/USP/INN)
- Fluoxymesterone [BAN:INN:JAN]
- Fluoxymesterone (JP15/USP/INN)
- HMS2272B06
- BCP10776
- NSC10704
- NSC12165
- Tox21_113158
- Tox21_200854
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [ORANGE BOOK]
- LMST02020025
- FLUOXYMESTERONE CIII [USP-RS]
- AKOS015895109
- CS-O-01553
- DB01185
- FLUOXYMESTERONE [USP MONOGRAPH]
- Fluoxymesterone, solid (photosensitive)
- NCGC00091037-01
- NCGC00091037-02
- NCGC00258408-01
- AC-29744
- LS-19496
- SMR000686158
- Fluoxymesterone 1.0 mg/ml in Acetonitrile
- D00327
- A838701
- Q410663
- W-104363
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta-hydroxy-17alpha-methyltestosterone
- (11-beta,17-beta)-9-Fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
- 9alpha-Fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17alpha-methylandrost-4-en-3-one
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-17-methyl-
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methyl-(VAN)
- 11-beta,17-beta-dihydroxy-9-alpha-fluoro-17-alpha-methyl-4-androsten-3-one
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 9-fluoro-11beta,17beta-dihydroxy-17-methyl-(VAN) (8CI)
- (1R,2S,10S,11S,14S,15S,17S)-1-fluoro-14,17-dihydroxy-2,14,15-trimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0;{2,7}.0;{11,15}]heptadec-6-en-5-one
- (8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,17S)-9-fluoranyl-10,13,17-trimethyl-11,17-bis(oxidanyl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one

