Tamoxifen Citrate Information
Click here to view all Tamoxifen Citrate productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
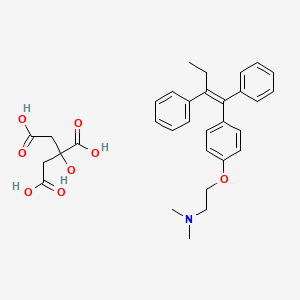
Tamoxifen citrate (also known as Nolvadex) is a medication that is commonly used in the treatment and prevention of breast cancer. It belongs to a class of drugs known as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs).
Anabolic steroid use can disrupt the body's natural hormonal balance, leading to elevated levels of estrogen. Tamoxifen citrate can help normalize hormone levels by blocking estrogen receptors and reducing estrogen activity. This may be particularly relevant during post-cycle therapy (PCT) when individuals attempt to restore their natural hormone production after a steroid cycle.
Tamoxifen works by binding to estrogen receptors in breast cancer cells, blocking the effects of estrogen. Estrogen is a hormone that can promote the growth of certain types of breast cancer. By blocking the estrogen receptors, tamoxifen inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells and prevents them from spreading.
In addition to its anti-estrogenic effects, tamoxifen also has estrogen-like effects on other tissues in the body, such as bone and the uterus. It can help prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women. However, tamoxifen can also increase the risk of uterine cancer, so regular gynecological check-ups are recommended for women taking this medication.
Tamoxifen citrate is usually taken orally in the form of tablets. The dosage and duration of treatment may vary depending on the individual's condition and response to the medication. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare professional for proper guidance and monitoring while taking tamoxifen.
Synonyms of Tamoxifen Citrate
- Tamoxifen citrate
- 54965-24-1
- Istubal
- Zitazonium
- Kessar
- Zemide
- Tamoxifen (Citrate)
- Tamoxifen citrate salt
- Caditam
- Farmifeno
- Ginarsan
- Jenoxifen
- Ledertam
- Nourytam
- Nourytan
- Noxitem
- Oncotam
- Tafoxen
- Tamofen
- Tamofene
- Tamoxasta
- Terimon
- Tomaxasta
- Zynoplex
- Emblon
- Nolgen
- Noltam
- Genox
- Tamax
- Tamox-Puren
- ICI 46474
- Z-Tamoxifen citrate
- ICI 46,474
- ICI 46474 citrate
- NSC-180973
- NSC-757345
- Tamoxifen Citrate (Nolvadex)
- Taxus
- I.C.I. 46474 citrate
- UNII-7FRV7310N6
- CCRIS 6718
- Apo-Tamox
- DTXSID8021301
- 54965-24-1 (citrate)
- 7FRV7310N6
- I.C.I.46474 CITRATE
- EINECS 259-415-2
- Tamoxifen citrate [USAN:USP:JAN]
- NSC180973
- NCGC00024928-06
- CAS-54965-24-1
- (Z)-2-(p-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethylethylamine citrate (1:1)
- Ethanamine, 2-[4-(1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-,2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)
- DTXCID101301
- C26H29NO.C6H8O7
- Tamoxifencitrate
- N,N-Dimethyl-2-(p-(1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)ethylamine citrate
- (Z)-2-[4-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine citrate
- Ethylamine, 2-(p-(1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethyl-, citrate (Z)-
- (Z)-2-(4-(1,2-diphenylbut-1-en-1-yl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- 2-[4-[(Z)-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl]phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
- SMR000677949
- SR-01000075523
- Tamoxifen citrate [USAN:JAN]
- Tamoxifeni citras
- trans-1-(p-beta-Dimethylaminoethoxyphenyl)-1,2-diphenylbut-1-ene citrate
- Soltamox (TN)
- (Z)-(2-(4-(1,2-Diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy)ethyl)dimethylammonium dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- (Z)-[2-[4-(1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethyl]dimethylammonium dihydrogen 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- Ethanamine, 2-(4-((1Z)-1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethyl-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)
- Ethanamine, 2-(4-(1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethyl, (Z)-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)
- Ethanamine, 2-[4-[(1Z)-1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl]phenoxy]-N,N-dimethyl-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)
- Prestwick_458
- MFCD00058321
- Tamoxifen (Nolvadex)
- Tamoxifen Citrate,(S)
- Tamoxifen, citrate salt
- Lopac-T-9262
- Tamoxifen Z-isomer citrate
- CHEMBL786
- SCHEMBL6365
- MLS001055370
- MLS002154210
- SPECTRUM1500557
- Nolvadex (TN) (AstraZeneca)
- C26H29NO.xC6H8O7
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [MI]
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [JAN]
- Tamoxifen citrate (JP17/USP)
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [USAN]
- HMS500M20
- Tamoxifen citrate salt, >=99%
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [VANDF]
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [MART.]
- GLXC-26314
- HMS1568M14
- HMS1921C13
- HMS2092K17
- HMS2095M14
- HMS2232E08
- HMS3263B08
- HMS3675P04
- HMS3712M14
- Pharmakon1600-01500557
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [USP-RS]
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [WHO-DD]
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [WHO-IP]
- 2-{4-[(1Z)-1,2-diphenylbut-1-en-1-yl]phenoxy}-N,N-dimethylethanamine 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate (salt)
- Ethanamine, 2-[4-(1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)
- EX-A5777
- hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- Tox21_110938
- Tox21_202070
- Tox21_300274
- Tox21_501203
- CCG-39629
- HB0602
- NSC757345
- s1238
- s1972
- AKOS005111126
- Tox21_110938_1
- CS-1852
- KS-5046
- LP01203
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [ORANGE BOOK]
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [EP MONOGRAPH]
- NCGC00016206-01
- NCGC00016206-02
- NCGC00016206-03
- NCGC00016206-04
- NCGC00016206-05
- NCGC00016206-06
- NCGC00024928-02
- NCGC00024928-23
- NCGC00094450-01
- NCGC00094450-02
- NCGC00094450-03
- NCGC00094450-04
- NCGC00254000-01
- NCGC00259619-01
- NCGC00261888-01
- TAMOXIFEN CITRATE [USP MONOGRAPH]
- TAMOXIFENI CITRAS [WHO-IP LATIN]
- HY-13757
- LS-68202
- BCP0726000223
- Tamoxifen Citrate - CAS 54965-24-1
- EU-0101203
- SW219368-1
- T2510
- (Z)-2-(4-(1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy)
- A19582
- D00966
- T 9262
- Q-201776
- SR-01000075523-1
- SR-01000075523-3
- SR-01000075523-5
- SR-01000075523-6
- Q27108378
- SR-01000075523-10
- (Z)-1-(4-Dimethylaminoethoxyphenyl)-1,2-diphenyl-1-butene Citrate
- Tamoxifen citrate, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- (z)-2-(4-(1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-n,n-dimethylethanamine,citrate
- Tamoxifen citrate, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
- (Z)-2-[ p-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]- N, N-dimethylethylamine citrate (1:1)
- (Z)-2-[4-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethyl-ethanamine cirtrate (1:1)
- Tamoxifen citrate for performance test, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- (2-{4-[1,2-diphenylbut-1-en-1-yl]phenoxy}ethyl)dimethylamine; 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
- (Z)-2-(4-(1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- {2-[4-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-buten-1-yl)phenoxy]ethyl}dimethylamine 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate salt
- 7244-97-5
- Etanamina, 2-[4-[(1Z)]-1,2-difenil-1-buten-1-il fenoxi]-N,N-dimetil-, 2-hidroxi-1,2,3-propanotricarboxilato (1: 1)
- Ethanamine, 2-(4-(1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate
- Ethanamine,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1)

