Testosterone Acetate Information
Click here to view all Testosterone Acetate productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
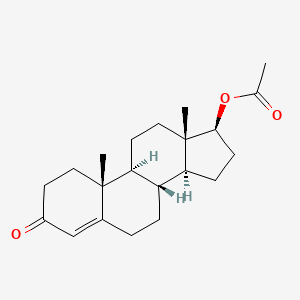
What is Testosterone Acetate?
Testosterone Acetate is a fast-acting ester of testosterone, belonging to the class of anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS). It is derived from testosterone by attaching an acetate ester to the testosterone molecule. The acetate ester allows for a rapid release of testosterone into the bloodstream after injection, leading to a quick onset of its effects.
However, it's important to note that Testosterone Acetate is not as widely available as other testosterone esters, such as Testosterone Enanthate or Testosterone Cypionate, which are more commonly used in medical and non-medical settings.
As with other forms of synthetic testosterone, Testosterone Acetate can have anabolic and androgenic effects. These effects can include increased protein synthesis, enhanced muscle growth, improved strength and endurance, and the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
However, like any anabolic steroid, Testosterone Acetate can also have potential side effects. These can include acne, oily skin, water retention, increased blood pressure, changes in cholesterol levels, suppression of natural testosterone production, testicular atrophy, and potential cardiovascular and liver-related risks.
How Testosterone Acetate works?
Testosterone Acetate works in a similar manner to other forms of testosterone by supplementing or replacing natural testosterone in the body. Here's how it works:
- Administration: Testosterone Acetate is typically administered via intramuscular injection. Once injected into the muscle, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream due to its fast-acting nature.
- Testosterone Release: Testosterone Acetate is an esterified form of testosterone, with an acetate ester attached to the testosterone molecule. This ester allows for a rapid release of testosterone into the bloodstream after injection, leading to a quick onset of its effects.
- Binding to Androgen Receptors: Once in the bloodstream, the released testosterone from Testosterone Acetate binds to androgen receptors in various tissues throughout the body. Androgen receptors are found in the cytoplasm of target cells, and when testosterone binds to them, it forms a testosterone-receptor complex.
- Translocation to the Nucleus: The testosterone-receptor complex moves into the cell nucleus, where it binds to specific DNA sequences called hormone response elements (HREs). This binding triggers a series of molecular events that modulate gene expression.
- Gene Expression: The testosterone-receptor complex bound to HREs initiates the transcription of specific genes. These genes are involved in various physiological processes, including protein synthesis, nitrogen retention, muscle growth, bone density regulation, red blood cell production, and the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
- Anabolic and Androgenic Effects: Testosterone Acetate exerts both anabolic and androgenic effects. The anabolic effects refer to its ability to promote protein synthesis, increase muscle mass, improve strength, and enhance recovery. The androgenic effects are responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics, such as facial and body hair growth, deepening of the voice, and increased libido.
It's important to note that the effects and risks associated with Testosterone Acetate, as with any form of testosterone or anabolic steroid, can vary depending on factors such as dosage, individual response, and overall health. The use of Testosterone Acetate should only be done under the supervision of a healthcare professional and in accordance with prescribed guidelines.
Synonyms of Testosterone Acetate
- Testosterone acetate
- 1045-69-8
- Deposteron
- Testosterone 17-acetate
- Farmatest
- Amolisin
- Aceto-sterandryl
- Aceto-testoviron
- Perandrone A
- Androtest A
- 17beta-Acetoxy-4-androsten-3-one
- Testosterone, acetate
- 17beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one acetate
- SKF 5647
- 3-Oxoandrost-4-en-17beta-yl acetate
- NSC 523836
- testosterone-17-acetate
- EINECS 213-876-6
- Androst-4-en-17beta-ol-3-one acetate
- 17-beta-(Acetyloxy)androst-4-en-3-one
- (17beta)-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one acetate
- CHEBI:16524
- (17-beta)-17-(Acetyloxy)androst-4-en-3-one
- UNII-5652105Y6S
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 17-(acetyloxy)-, (17beta)-
- 17.beta.-Acetoxy-4-androsten-3-one
- [(8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] acetate
- 3-Oxoandrost-4-en-17.beta.-yl acetate
- 17beta-acetoxy-Delta(4)-androstan-3-one
- 5652105Y6S
- 17beta-hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one, 17-acetate
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 17-(acetyloxy)-, (17-beta)-
- 3-Oxoandrost-4-en-17beta-yl Acetate (Testosterone Acetate)
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 17-(acetyloxy)-, (17.beta.)-
- Testosteron-acetat
- NSC-523836
- Androst-4-en-17.beta.-ol-3-one acetate
- 17.beta.-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one acetate
- Testosterone acetic acid
- Testosterone 17-O-Acetate
- Testosterone 17-acetic acid
- SCHEMBL547898
- CHEMBL488762
- 17b-Acetoxy-4-androsten-3-one
- DTXSID80909007
- TESTOSTERONE ACETATE [MI]
- 4-Androsten-17-ol-3-one acetate
- BCP10771
- LMST02020057
- TESTOSTERONE ACETATE [WHO-DD]
- 4-androsten-17beta-yl acetate-3-one
- AKOS015914033
- AM84320
- 17b-Acetoxy-delta(4)-androstan-3-one
- 17b-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one acetate
- AS-75507
- 17b-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one acetic acid
- LS-148814
- TESTOSTERONE IMPURITY E [EP IMPURITY]
- 17.beta.-Acetoxy-.DELTA.4-androstan-3-one
- 17beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one acetic acid
- C03027
- Q27101955
- TESTOSTERONE ACETATE IMPURITY A [EP IMPURITY]

