Testosterone Decanoate Information
Click here to view all Testosterone Decanoate productsThe information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
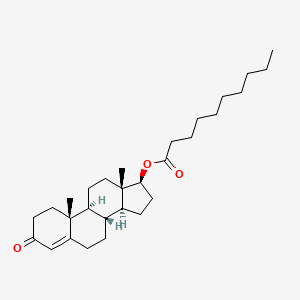
What is Testosterone Decanoate?
Testosterone Decanoate is an esterified form of the hormone testosterone, which is naturally produced in the human body. It is one of the many testosterone esters commonly used in the field of medicine and bodybuilding.
Testosterone Decanoate is classified as an androgen and anabolic steroid. It acts as a prodrug, meaning it is converted into its active form, testosterone, after administration. The decanoate ester attached to the testosterone molecule slows down its release into the bloodstream, resulting in a prolonged and sustained release of testosterone.
Here are some key details about Testosterone Decanoate:
- Medical Uses: Testosterone Decanoate is primarily used for hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in men with low testosterone levels. It can help treat conditions such as hypogonadism, where the body fails to produce sufficient testosterone. It may also be used in the treatment of certain breast cancers in women.
- Bodybuilding and Performance Enhancement: Due to its ability to increase muscle mass, strength, and enhance athletic performance, Testosterone Decanoate is sometimes used illicitly by bodybuilders and athletes. However, it is important to note that such use is typically considered illegal and against the regulations of most sporting organizations.
- Administration and Dosage: Testosterone Decanoate is typically administered via intramuscular injection. The dosage and frequency of administration can vary depending on the specific medical condition being treated or the desired performance enhancement goals. It is crucial to follow the advice and guidance of a qualified healthcare professional when using this substance.
- Side Effects: Testosterone Decanoate, like other forms of testosterone, can cause a range of side effects. These may include acne, oily skin, increased body and facial hair growth, male pattern baldness, changes in libido, mood swings, water retention, liver toxicity, and suppression of natural testosterone production. Additionally, the use of testosterone in high doses or for prolonged periods can lead to more serious health issues, such as cardiovascular problems and liver damage.
- Legal Status: The use of Testosterone Decanoate without a valid medical prescription is considered illegal in many countries. It is classified as a controlled substance and falls under the category of anabolic steroids.
It is important to emphasize that the use of Testosterone Decanoate or any anabolic steroid without proper medical supervision can have serious health consequences. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on the safe and appropriate use of such substances.
How Testosterone Decanoate works?
Testosterone Decanoate works by delivering exogenous testosterone to the body. Once injected, the decanoate ester attached to the testosterone molecule slows down its release into the bloodstream. As a result, testosterone is gradually released over an extended period.
When testosterone is released into the body, it binds to androgen receptors in various tissues, including muscle cells. This binding activates specific cellular mechanisms that promote anabolic (muscle-building) effects. Here's a breakdown of how Testosterone Decanoate works:
- Androgen Receptor Activation: Testosterone binds to androgen receptors located within the target tissues, such as skeletal muscle cells. This interaction initiates a cascade of cellular events.
- Transcriptional Regulation: Once testosterone binds to the androgen receptor, it undergoes a structural change that allows it to enter the cell nucleus. Inside the nucleus, the testosterone-androgen receptor complex acts as a transcription factor, influencing gene expression.
- Protein Synthesis: Testosterone promotes protein synthesis, leading to increased production of muscle proteins. This anabolic effect contributes to muscle growth, improved recovery, and enhanced strength.
- Nitrogen Retention: Testosterone also improves nitrogen balance in the body. Nitrogen is an essential component of proteins, and maintaining a positive nitrogen balance supports muscle growth and prevents muscle breakdown (catabolism).
- Enhanced Red Blood Cell Production: Testosterone can stimulate the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Increased red blood cell count improves oxygen-carrying capacity, endurance, and overall performance.
- Increased IGF-1 Production: Testosterone can enhance the production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a hormone that promotes tissue growth and repair. IGF-1 has an anabolic effect on muscle cells, further contributing to muscle growth.
It's important to note that Testosterone Decanoate, like other forms of exogenous testosterone, can suppress the body's natural testosterone production. This occurs because the presence of exogenous testosterone signals the body to reduce its own production. After discontinuing Testosterone Decanoate use, a period of post-cycle therapy (PCT) may be necessary to help restore natural testosterone production.
Furthermore, it's crucial to recognize that the use of Testosterone Decanoate or any other anabolic steroid without proper medical supervision can lead to health risks and adverse effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for ensuring safe and responsible use of such substances.
Synonyms of Testosterone Decanoate
- Testosterone decanoate
- 5721-91-5
- UNII-IJW60LAO6S
- IJW60LAO6S
- [(8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] decanoate
- 17beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one decanoate
- DTXSID5046198
- CHEBI:35000
- EINECS 227-226-4
- NSC 26642
- NSC-26642
- NCGC00160513-01
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 17-[(1-oxodecyl)oxy]-, (17b)-
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 17-[(1-oxodecyl)oxy]-, (17.beta.)-
- Test Decanoate
- Testosterondecanoat
- Testocaps (TN)
- testosterone caprate
- Testosterone caprinate
- Testosteroen Decanoate
- Testosterone 17beta-decanoate
- SCHEMBL219795
- GTPL7630
- CHEMBL1473654
- DTXCID3026198
- BCP17658
- NSC26642
- Tox21_111863
- AKOS015895429
- TESTOSTERONE DECANOATE [MART.]
- CS-O-30806
- DS-3319
- TESTOSTERONE DECANOATE [WHO-DD]
- CAS-5721-91-5
- TESTOSTERONE DECANOATE [EP MONOGRAPH]
- (17beta)-3-Oxoandrost-4-en-17-yl decanoate
- D08573
- 3-OXOANDROST-4-EN-17.BETA.-YL DECANOATE
- W-105480
- 17.BETA.-HYDROXYANDROST-4-EN-3-ONE DECANOATE
- Q27088963
- Androst-4-en-3-one, 17-((1-oxodecyl)oxy)-, (17beta)-
- Androst-4-en-3-ona, 17-[(1-oxodecil)oxi]-, (17beta )-
- Testosterone decanoate, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- Testosterone decanoate for system suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
- (1S,3aS,3bR,9aR,9bS,11aS)-9a,11a-dimethyl-7-oxo-1H,2H,3H,3aH,3bH,4H,5H,7H,8H,9H,9aH,9bH,10H,11H,11aH-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-yl decanoate

